|
Sator Square
Name of a remarkable Latin palindromic word square
consisting of five words, i.e. SATOR, AREPO, TENET, OPERA, and ROTAS,
arranged in a five-by-five grid that can be read in multiple directions,
horizontally, vertically, forwards, and backwards, while retaining the
same sequence of letters. The square usually appears in the form as
shown in the picture below. Each word contains five letters, forming a
perfectly symmetrical pattern of twenty-five characters. The literal
meanings of the words are as follows: Sator means “sower” or “creator”,
Arepo is a mysterious term found nowhere else in Latin and is either a
surname or may have been invented for the sake of symmetry, Tenet means
“holds” or “keeps”, Opera translates as “work” or “effort”, and Rotas
means “wheels”. The most straightforward translation of the whole
sentence would therefore be “The sower Arepo holds the wheels with
effort”, though this interpretation remains uncertain due to the obscure
nature of Arepo. The earliest known examples of the Sator Square have
been discovered in the Roman city of Pompeii, preserved in graffiti that
predates the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Subsequent examples
have been found across the Roman world, including in Dura-Europos in
Syria, Cirencester in England, and later in medieval churches in France
and Italy. Its widespread distribution suggests that it was known for
centuries and served various functions ranging from decorative
inscriptions to symbols of religious or magical significance. Scholars
have long debated the true meaning of the square. Some have interpreted
it as an agricultural proverb, referring to a farmer who controls his
plough and wheels with skill and diligence. Others regard it as a
philosophical or cosmological statement about divine order, in which the
“sower” represents a creator who governs the revolving “wheels” of the
universe. In the Christian era, the square acquired an additional layer
of interpretation. By rearranging its letters, one can form a cross
composed of the words PATER NOSTER, meaning “Our Father” in Latin,
leaving two As and two Os unused. These remaining letters have been read
as Alpha and Omega, the first and last letters of the Greek alphabet and
a well-known symbol of Christ’s eternity. This discovery led to the
hypothesis that early Christians used the Sator Square as a secret
symbol of faith, particularly during times of persecution. Beyond its
religious connotations, the Sator Square was also employed in magical
and folk traditions throughout Europe. It was often inscribed on
buildings, doors, and amulets as a protective charm believed to ward off
evil spirits, fire, and disease. In medieval manuscripts it sometimes
appeared alongside other apotropaic symbols and prayers, suggesting its
use as a talisman of cosmic balance and harmony. The perfection of its
symmetry may have been regarded as reflecting the order of the universe,
a quality thought to repel chaos and misfortune. Over the centuries the
Sator Square has continued to fascinate scholars, linguists, and
theologians alike. Its origins remain uncertain, its grammatical
coherence questionable, and its symbolic meanings multifaceted. Whether
viewed as a linguistic puzzle, a coded Christian emblem, or a magical
charm, it stands as one of the most intriguing and enduring word
patterns of the ancient world. Even today it continues to appear in art,
literature, and popular culture, often serving as a symbol of mystery,
symmetry, and hidden knowledge.

Schism of 1054
The Great Schism of 1054, also called the
East–West Schism, was the formal division between the
Roman Catholic Church
in the West and the
Eastern Orthodox Church
in the East. It was the culmination of centuries of theological,
political, cultural, and liturgical differences between Latin-speaking
Western
Christianity
and Greek-speaking Eastern
Christianity.
Central theological disputes included the
Filioque clause in the
Nicene Creed and differing views on
papal authority. The schism was marked by mutual excommunications
between Pope Leo IX and Patriarch Michael I Cerularius in 1054. While
attempts at reconciliation occurred over subsequent centuries, this
event established the enduring separation between the two branches of
Christianity.
Septuagint
Latin. Name of the Koine Greek version of the
Hebrew Bible, the oldest of several ancient translations of the original
Hebrew scripture into the Greek language. This was done in stages, between the 3rd and 1st centuries BC,
in Alexandria. The name, meaning “seventy”, derives from the traditional
idea that
seventy Jewish scholars made its translation, for Ptolemy II Philadelphus
(285–246 BC).
It is therefore also simply called LXX. The Septuagint includes some
books not found in the Hebrew Bible, which the Eastern Orthodox Churches
have also incorporated in their canon, whilst many Protestant Bibles follow
the Jewish canon, excluding these additional books. The Roman Catholic
Church uses only some of the additional books.
Seth (שֵׁת)
Hebrew. Name of a figure in the Hebrew Bible, the
third son of
Adam
and
Eve, born after
the death of Abel and the exile of Cain (Genesis 4:25). His name derives
from the Hebrew root šît (שִׁית), meaning
“appointed” or “placed”,
reflecting Eve’s statement that God had appointed him as a replacement
for Abel. Seth is portrayed as the ancestor of a righteous line of
humanity, from whom
Noah and, according to biblical genealogies, all
postdiluvian humanity descend (Genesis 5:3–32). In the genealogical
framework of Genesis, Seth’s descendants are presented as those who “walked with God” (Genesis 5:24), in contrast to the line of Cain,
emphasizing continuity of piety and divine favour. Jewish, Christian,
and Islamic traditions regard Seth as a patriarch and a symbol of moral
renewal, linking him to the preservation of human lineage and worship
after the fall, and he is often associated with the transmission of
knowledge, ritual, and devotion in early human history..
Shabbat
(שַׁבָּת)
Hebrew for the Sabbath, the seventh day of the
Jewish week and a day of complete rest, study and special worship,
observed from sunset Friday evening to sundown Saturday evening, though
some festivals, in Hebrew known as chagim (חַגִּים), are also
considered to be Shabbatot (Sabbath days), regardless of the day of the
week on which they fall. One who traditionally observes the legal
requirements for Shabbat is called Shomer Shabbat (שׁוֹמֵר שַׁבָּת). One
of the Ten Commandments requires the sanctification of this day. The
word is derived from the Hebrew verb shavat (שׁבת), meaning
“to cease
[from work]”, although it is commonly translated as “(to) rest”.
Shem (שֵׁם)
Name of a figure in the Hebrew Bible, the eldest
son of
Noah and one of the three
patriarchs through whom postdiluvian humanity is descended (Genesis
5:32; 6:10). His name derives from the Hebrew word šēm (שֵׁם), meaning
“name” or “renown”, reflecting the idea of an enduring legacy. Shem is
traditionally regarded as the ancestor of the Semitic peoples, including
the Hebrews, Arameans, Assyrians, and Arabs, and his lineage is
carefully recorded in Genesis 10 and 11, forming part of the Table of
Nations. Biblical narratives emphasize Shem’s role in preserving the
covenantal line after the Flood and his importance in the genealogical
framework linking
Noah to Abraham and subsequent
Israelite history. Jewish, Christian, and Islamic traditions recognize
Shem as a righteous patriarch, often associated with piety, continuity
of faith, and the establishment of God-favored nations.
Sisera (סיסרא)
Hebrew. Captain of Jabin's army who, after his
troops were destroyed by the army of Barak in the valley of Jezreel,
fled to the settlement of Heber the Kenite in the plain of Zaanaim.
There Jael, Heber's wife, received him into her tent with deceptive
hospitality, giving him some milk to drink. After this he lay down
exhausted and soon sank into a deep sleep. Whilst he lay asleep, Jael
sneaked up to him, took a hammer and forcefully drove one of the tent
pegs through his temples, killing him on the spot.

Supreme Governor of the Church of England
The official title held by the reigning monarch of
the United Kingdom, signifying their formal authority over the
Church of England,
including oversight of its governance and appointments, established
during the English
Reformation
when King Henry VIII separated the church from papal authority; the role
is largely ceremonial today, with spiritual leadership vested in the
Archbishop of Canterbury and the
episcopal hierarchy.
Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke, the first
three books of the canonical New Testament, so called because they
display a high degree of similarity. The word synoptic derives from the
Greek word synopsis (συνόψις), meaning
“giving a similar summary or
outline”, a word which itself is related to the word opse (όψη),
signifying “view” and “likeness”. The term refers to fact that those
three gospels share the same theme, point of view, content, order of
events and style, and differ significantly from the fourth gospel, i.e.
the gospel according to John.
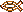 |